Would you like to be treated by AI machines or by humans for your ailments? Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used in healthcare to support diagnosis, improve patient outcomes, streamline operations and to even accelerate drug discovery. However, alongside its promise, AI in healthcare raises important questions about safety, ethics, equity and governance. This article explores the diverse applications of AI in healthcare, analyses its relevance with case studies of global examples of AI in healthcare and in India.
- Highlights
- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- The Need for AI in Healthcare
- Understanding the Role of AI in Healthcare
- How is AI Used in Healthcare
- AI in Medical Diagnosis and Imaging
- AI in Pathology and Laboratory Testing
- AI in Medical Screening and Early Detection
- AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems
- AI in Remote Patient Care and Monitoring
- AI in Drug Discovery and Research
- AI in Medical Administrative Applications
- Global Case Studies of AI in Healthcare
- Examples of AI in Healthcare in India
- Benefits of AI in Healthcare
- Limitations and Risks
- Regulation and Ethical Considerations
- Will AI in Healthcare Make Doctors Redundant?
- The Future of AI in Healthcare
- A Life Without Disease Is Possible
- FAQs
Highlights
- Misdiagnosis and privacy breach are among the top concerns of patients about the use of AI in healthcare as per the 2022 study by the Yale School of Medicine.
- Despite the lack of consumer confidence, the global healthcare market with generative AI is predicted to expand to USD 39.8 billion by the end of 2035, as published by the Global News Wire.
- Currently, North America leads the global market for AI in healthcare.
- India has been recently included in the HealthAI Global Regulatory Network (GRN), marking its position as a pioneer in the use of AI in healthcare.
- Grand View Research predicts India’s healthcare market touching USD 8728 million by 2030.
- Despite tech giants and the medical fraternity pushing hard for the use of AI in healthcare, privacy issues remain AI’s biggest challenges over the years.
- Could there be a way of escaping diseases altogether?
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands for computer systems built to mimic human intelligence. AI systems rely heavily on extensive data to gather information about various tasks to be able to understand and decipher human language, thereby attempting to mimic human reasoning and decision making abilities. AI is increasingly itself a vast field and works on multiple models. AI in healthcare typically uses machine learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP).
The Need for AI in Healthcare
AI in healthcare is not a new proposition. The intent to use robots, to automate medical diagnosis, to analyse data better, etc., has been on the agenda of the medical and tech industry for years. But the pressing need to accelerate work in AI in healthcare was felt only a few years ago.
The biggest challenges hit the medical fraternity hard during the COVID-19 pandemic when medical facilities were overburdened with an overflowing number of patients – a situation that prompted the medical fraternity to turn to AI in healthcare more aggressively.
Understanding the Role of AI in Healthcare
AI in healthcare has proved to be both useful and difficult at the same time. Before understanding the pros and cons, we will examine how AI contributes to the healthcare industry and its various applications.
Which AI is Used in Healthcare?
AI in healthcare typically involves machine learning (ML), deep learning, natural language processing (NLP) and also large language models (LLMs). These technologies are applied to clinical data such as imaging, pathology slides, genomic information and electronic health records.
Depending on the application, AI can function as:
- Diagnostic tools: They assist or automate the interpretation of scans, lab slides or monitoring data.
- Predictive systems: These forecast the risk of hospital readmissions, disease progression or treatment responses.
- Decision support: These healthcare AI systems suggest potential treatment options or triage patients based on severity.
- Operational tools: Such AI systems help in hospital operations like managing schedules, billing or supply chains.
- Discovery platforms: AI healthcare platforms that assist in speeding up drug design, identifying biomarkers or for analysing genomics.
How is AI Used in Healthcare
Here will examine various applications of AI in healthcare:
AI in Medical Diagnosis and Imaging
Medical imaging is one of the most advanced fields for AI adoption. Algorithms can help in predictive analysis in healthcare by analysing radiology scans, dermatology images and retinal photographs with high accuracy. They assist radiologists by prioritising urgent cases and sometimes match or even surpass expert performance in controlled studies. For example, AI has been trained to detect lung nodules on CT scans or identify melanoma in dermatology photographs.
AI in Pathology and Laboratory Testing
AI-powered microscopes and digital pathology platforms automate blood, urine and tissue analysis. This speeds up workflows and reduces error rates in high-volume laboratories. The result is faster diagnoses and reduced strain on human pathologists.
AI in Medical Screening and Early Detection
Portable AI-based medical devices are aiding mass screening. They can be deployed in community health camps or rural clinics, offering low-cost solutions for detecting diseases like diabetic retinopathy, tuberculosis or breast cancer.
AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems
By analysing patient histories, lab results and imaging together, AI can alert doctors to potential risks such as sepsis, suggest possible diagnoses, or recommend personalised treatments.
AI in Remote Patient Care and Monitoring
Wearables integrated with AI algorithms can perform functions like a nurse. They can detect irregular heart rhythms, predict asthma attacks or monitor blood glucose trends. Such AI systems can be helpful for managing chronic illnesses remotely and preventing emergency admissions.
AI in Drug Discovery and Research
Pharmaceutical companies now rely on AI to identify potential drug molecules, simulate their behaviour and thereby, design efficient clinical trials. This reduces development time and costs, potentially bringing therapies to market faster.
AI in Medical Administrative Applications
AI can reduce the clerical load on hospital administration through tools that automate medical transcription, billing and record-keeping. Natural language processing allows quick summarisation of patient notes and discharge reports.
Global Case Studies of AI in Healthcare
Let us look at three important cases of AI driven-systems developed for medical diagnostics.
IDx-DR (United States)
The FDA cleared this AI system to autonomously detect diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans, without requiring an ophthalmologist to interpret the results. This approval was believed to be historic, as it demonstrated that AI could directly participate in frontline patient care. However, there are some limitations to this AI software. It cannot be used in early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Also, the patient must be more than 22 years of age.
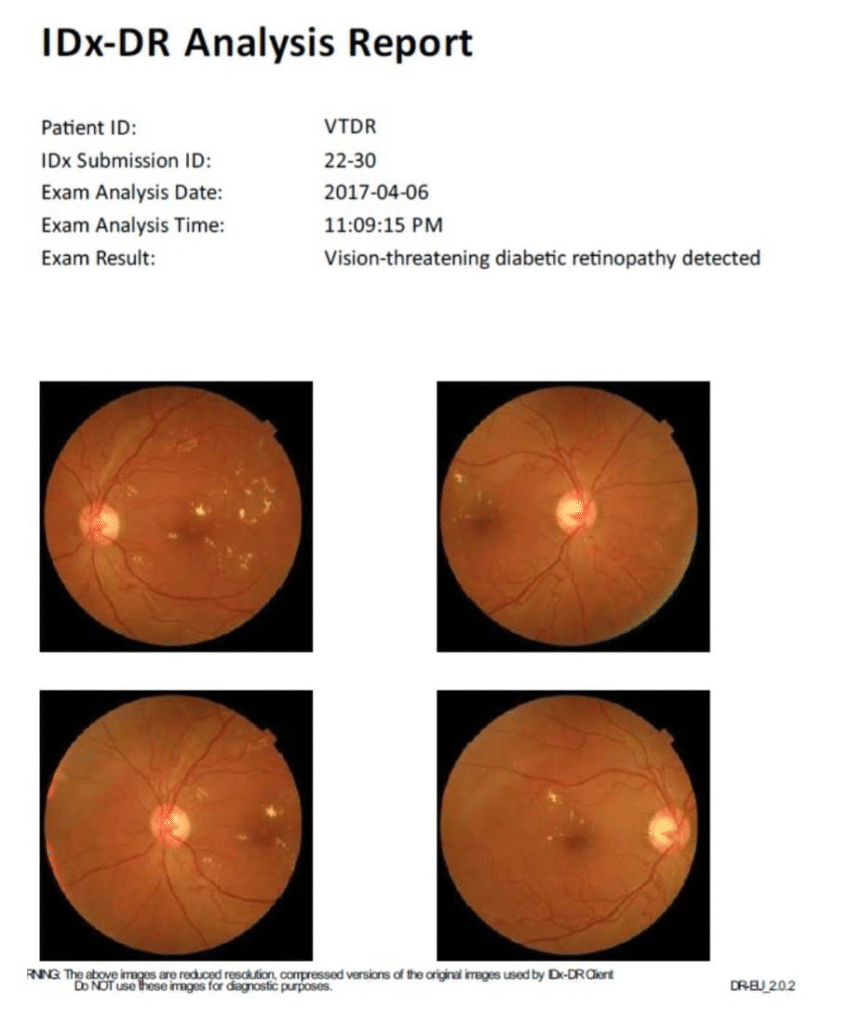
Image Title: A Sample Diagnostic Report by IDx-DR (Image courtesy Healthvisors)
DeepMind and Moorfields Eye Hospital (UK)
Researchers developed AI that could detect a wide range of eye diseases from retinal scans. The project showcased how large datasets and advanced algorithms could support ophthalmologists, but also highlighted the need for strong data governance when handling sensitive patient records. DeepMind and Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation partnered to build this AI system. Google Health has now acquired DeepMind, and the arrangement with Moorfields Eye Hospital continues.
Moorfields Eye Hospital revealed that as many as a minimum of 5000 OCT scans were done in their hospital each week. Their partnership with DeepMind is an attempt to reduce the time taken to analyse these scans and detect eye diseases early on.
IBM Watson for Oncology
Once hailed as a breakthrough, this system struggled in real-world use, sometimes offering unsafe or irrelevant recommendations. The project illustrated the risks of deploying AI before it is clinically validated, serving as a cautionary tale. IBM Watson couldn’t directly process structured data and required heavy maintenance, leading to it being shelved completely.
Examples of AI in Healthcare in India
India’s healthcare challenges are large population, shortage of specialists and rural-urban disparities. This gives AI a chance in attempting to fill in the void that still needs to be covered. Several Indian companies and initiatives are building solutions such as:
Thermalytix by Niramai
Niramai developed an AI-based breast cancer screening test ‘Thermalytix’ that uses thermal imaging instead of mammography. The system is portable, radiation-free and cost-effective. Niramai states it is suitable for community-level screening, especially in rural India, and also for mass corporate screenings where corporates organise health check up camps for employees. State governments and NGOs have already deployed it in health camps.
Also Read: H3N2 Virus Surge in Delhi-NCR: Symptoms, Risks, and Precautions
Niramai claims that Thermalytix reduces the scope of human error and subjectivity in decision-making. Thermalytix has been trained for histopathy, mammography and ultrasound.
SigTuple
SigTuple Technologies Private Limited is a Bengaluru-based startup that uses AI to automate analysis of blood smears, urine samples and other laboratory slides. Their aim is to create better AI-powered screening solutions. By reducing dependence on human technicians, SigTuple seeks to make diagnostic services more accessible and reliable. They use cloud computing, AI and robotics as the base for their softwares.

Image Title: SigTuple’s AI100 robotic microscope (Image courtesy SigTuple)
Government Pilots
Several state health departments are experimenting with AI-based screening for cervical cancer, diabetic retinopathy. and tuberculosis. The Government of India has also ventured into AI in telemedicine with its eSanjeevani platform.
Under the public and private sector partnerships, the Government of India has also collaborated with IIT Kanpur via the National Health Authority (NHA) to develop AI in healthcare.
India being welcomed to join the HealthAI Global Regulatory Network (GRN) is seen as a major feather in India’s cap in this segment. The announcement made by the Ministry of Electronics and IT on 4th September 2025 reveals that India will work together with HealthAI to share best practices and information. Read the press release issued by the Ministry of Electronics and IT here.

Image Title: Indian Joins HealthAI Global Regulatory Network (GRN)
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
Though there are more challenges than benefits of AI in healthcare, here are some advantages:
- Improved Access Due to Portability: AI-powered portable devices bring advanced diagnostics to rural and underserved areas.
- Faster Process: Automation speeds up lab reports, imaging interpretation and hospital administration, to name a few.
- Consistency: AI claims to offer standardised results, reducing variability between human readers. However, these claims are debated.
- Personalised Care: Predictive models can tailor treatments to an individual’s genetic and clinical profile.
- Cost Savings: Early detection and automation can reduce the expenses of late-stage treatment on the part of the patient and manual labour on the part of the hospital.
Limitations and Risks
Despite these advantages, challenges remain as follows:
- Bias in Data: If training datasets underrepresent certain populations, AI systems may produce less accurate results for them, reinforcing health inequalities. Datasets bias has been a concern in not just healthcare, but several other segments with AI.
- Explainability Issues: Many AI systems offer results without clear reasoning. Medical experts hesitate to trust such outputs.
- Clinical Validation Gap: Systems that perform well in controlled studies often fail to replicate results in real-world settings.
- Legal and Regulatory Ambiguity: Questions about accountability arise, for example, if an AI gives a wrong diagnosis, who is liable? Is it the doctor, the developer or the hospital?
- Privacy Concerns: Medical data is highly sensitive, and breaches could have serious consequences. Strong safeguards are needed. Data privacy has been a steady concern with AI.
- Hype versus Reality: Overpromising can erode trust. The failure of IBM Watson for Oncology reminds us that AI must be evidence-based and not marketing-driven.
Regulation and Ethical Considerations
Internationally, regulators such as the FDA and European Medicines Agency are creating pathways for AI-based medical devices. In January 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued guidelines for AI ethics and government governance with emphasis on transparency, equity and human oversight. This was reiterated in WHO’s March 2025 release of an extensive publication on AI ethics and governance. Read about the complete set of WHO guidelines here.
In India, the Ministry of Health and the NITI Aayog think tank have expressed interest in establishing AI governance frameworks. Local guidelines will be essential to ensure AI tools deployed in India are validated for local populations and implemented responsibly.
Will AI in Healthcare Make Doctors Redundant?
AI can attempt to mimic human intelligence but not replace it completely where humans touch is necessary. Though AI systems in healthcare promise effective diagnosis and in some cases, treatments too, they cannot replace doctors in complicated decision-making cases. Additionally, in cases with a complex patient history, a doctor’s experience is necessary.
Similarly, in the case of nurses, where a human touch and emotional support is required, AI cannot replace nurses. While industry experts do believe that the increasing deployment of AI will certainly affect jobs in the medical sector, it may also bring in new opportunities of overseeing AI processes.
How a balance is maintained between technology and employment is also on the part of the governments and regulating bodies.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI technology in medicine depends on several factors. However, it is important to understand that AI is not a replacement for doctors or nurses, but an ally. Aside from the various challenges of AI in healthcare, the one that is often less addressed is the acceptance of patients. Do patients really want to be treated by AI machines? Or do they prefer a real human doctor to interact with? The AI industry and the medical fraternity seem to be sidelining this important aspect.
What if there truly was a way to escape diseases altogether? Imagine a life where there is no dependence on doctors, no reliance on artificial intelligence and no fear of falling ill. A life of pure health and freedom. For many, this may sound far-fetched, even impossible. However, this is the lived reality of the disciples of Jagatguru Tatvdarshi Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj.
The divine way of worship bestowed by Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj carries a power that transcends human understanding. Innumerable disciples testify that by simply following the spiritual practice shown by Him, they have been freed from chronic illnesses, even from life-threatening diseases such as cancer. These are not isolated stories but widespread experiences that science struggles to explain.
Is this sorcery? Certainly not. It is something infinitely higher, something far superior to the technologies the world clings to in desperation. While humanity continues to place its faith in machines and algorithms, Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj reveals a path of true worship that heals not just the body, but also the soul. It is here that one discovers the ultimate cure for a disease-free life granted by the Almighty through authentic spiritual practice.
A Life Without Disease Is Possible
Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj has given countless disciples a new lease of life by curing them of deadly and ‘incurable’ diseases such as cancer and AIDS. They have been cured not through medical intervention, but through the divine way of worship that is clearly validated in our holy scriptures. This unmatched method of devotion is not just a remedy for health issues, it is the master key that unlocks solutions to every problem in life.
Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj reveals that the true root of all disease is not found in diet, genetics or lifestyle, but in karma. This world is ruled by the law of karma, and unless those karmas are cleansed, suffering will persist. The only path to freedom is to worship Supreme God Kabir under the guidance of Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj, the one true Tatvdarshi Saint of this age.
Thousands have already witnessed miracles in their own lives. From healing of life-threatening diseases to resolution of struggles that seemed impossible, disciples across the world testify to the transformative power of this worship. Skeptics may question, but they cannot ignore the sheer weight of living evidence.
The miracles you once thought belonged only to ancient times are unfolding today before our very eyes. Why wait in hope when the path to a disease-free, worry-free and blissful life is open? Discover the worship that changes destinies. Take refuge in Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj and experience the miracle of true devotion for yourself. For more information, visit:
- Website: www.jagatgururampalji.org
- YouTube channel: Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj
- Facebook page: Spiritual Leader Saint Rampal Ji
- ‘X’ handle: @SaintRampalJiM
FAQs
Q1: How AI in healthcare works?
Answer: AI in healthcare is used in multiple medical fields such as diagnostics, screening, data analysis, to name a few.
Q2: Can AI replace doctors?
Answer: AI can never replace doctors, though it may assist doctors.