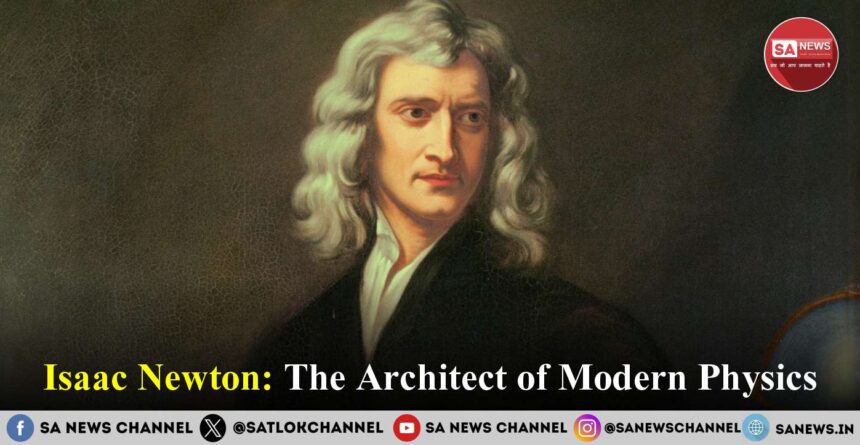
Isaac Newton, who was born on January 4, 1643, in Woolsthorpe, Lincolnshire, England, stands as one of the most significant individuals in the annals of scientific history. His groundbreaking discoveries in physics, optics, and mathematics revolutionized our understanding of the natural world and laid the foundation for modern scientific thought.
Early Life and Education
From a young age, Newton faced adversity and hardship. His father died prior to his birth, and following this, his mother entered into a new marriage, resulting in him being raised by his grandmother. Despite these challenges, Newton’s innate curiosity and intellect shone through. He attended the King’s School in Grantham, where he developed a passion for learning and a keen interest in mechanics and mathematics. In 1661, he enrolled at the University of Cambridge’s Trinity College, where his scientific journey truly began.
Newton’s Contributions to Science
Isaac Newton: Newton’s contributions to science are monumental and far-reaching. His three laws of motion laid the foundation for classical mechanics, describing the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. These laws are still taught in physics classes around the world and are fundamental to our understanding of how objects move.
- First Law of Motion:
commonly referred to as the law of inertia, asserts that an object will continue to be at rest or maintain a constant velocity unless influenced by an external force - Second Law of Motion:
The second law quantifies the effect of force on an object’s motion, stating that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object times its acceleration (F = ma). - Third Law of Motion:
The third law, famously known as “for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction,” explains the mutual forces of action and reaction between two interacting objects.
The Law of Universal Gravitation
Isaac Newton: One of his most renowned contributions is the law of universal gravitation. Newton suggested that every mass in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other mass, with the strength of this force being directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them. This revolutionary theory elucidated not only the movements of celestial bodies but also the phenomenon of an apple descending from a tree, a narrative frequently linked to Newton’s moment of discovery.
■ Also Read: The Cosmic Genius: Albert Einstein’s Journey & Biography
Contributions to Optics
In the field of optics, Newton made significant strides. He discovered that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors, which can be separated and recombined using a prism. This work laid the groundwork for modern physical optics and changed our understanding of light and color.
Contributions to Mathematics
Newton also made substantial contributions to mathematics. He independently developed infinitesimal calculus, a major advancement that provided the tools needed to describe changing quantities. This mathematical framework is essential in many fields of science and engineering today.
Legacy and Impact
Newton’s most notable works include the “Principia,” published in 1687. This seminal work details his laws of motion and universal gravitation and is considered one of the most important works in the history of science. Despite his complex personality, Newton’s dedication to his research and his relentless pursuit of knowledge were key to his success.
Isaac Newton’s impact on science and society is profound and enduring. His discoveries in physics, optics, and mathematics have shaped our understanding of the universe and continue to influence scientific thought and research. Newton’s life serves as an inspiration to all who seek to explore the mysteries of the natural world, reminding us of the importance of curiosity, dedication, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj: Harmonizing Science and Spirituality to Achieve Supreme God
Sant Rampal Ji Maharaj believes that scientific discoveries and spiritual insights together enhance our understanding of the universe and the Supreme God. He argues that the complexity in science indicates a higher intelligence, fostering respect for the Creator.
He emphasizes that “Tatv Gyan,” or genuine knowledge, is essential for spiritual freedom, merging scientific and spiritual truths to guide individuals toward salvation and Satlok, the eternal home of the Supreme God. By appreciating science and adhering to truth, one can advance spiritually. Ultimately, He views scientific discoveries as tools that deepen our connection with the divine, helping individuals unite with the Supreme God.