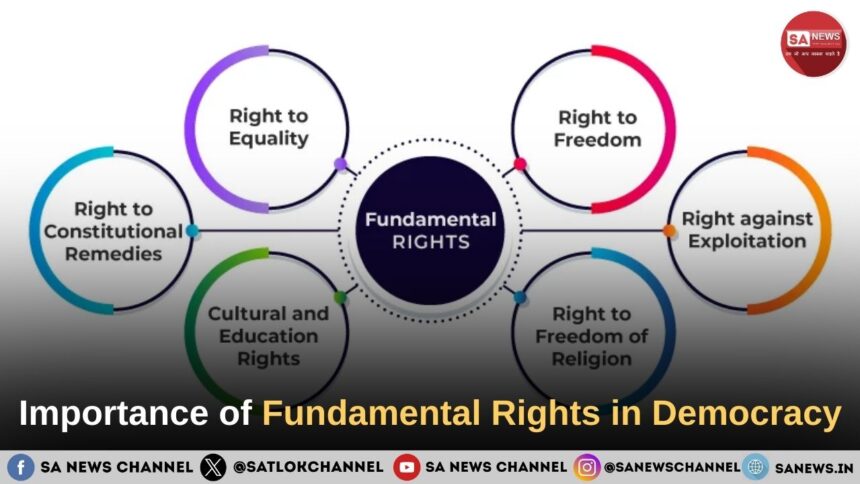
Fundamental Rights in Democracy: In a democratic nation, the Constitution stands as the supreme legal authority that defines the structure of governance and safeguards the liberties of citizens. Among its most significant provisions are the Fundamental Rights, which serve as the foundation of democracy. These rights are essential not only for protecting individual freedom but also for ensuring justice, equality, and dignity for all. Without Fundamental Rights, democracy would lose its true spirit and could gradually shift toward authoritarianism. Therefore, understanding the importance of Fundamental Rights is crucial for preserving democratic values and strengthening national unity.
- Historical Evolution of Fundamental Rights:
- Nature and Features of Fundamental Rights:
- Right to Equality: Cornerstone of Justice
- Right to Freedom:
- Right against Exploitation:
- Right to Freedom of Religion:
- Cultural and Educational Rights:
- Right to Constitutional Remedies: Enforcement Mechanism
- Judicial Interpretation and Expansion:
- Role in Social Transformation:
- Contemporary Relevance in the Digital Era:
- Challenges in Realization:
- Fundamental Rights and Democratic Culture:
- Global Context:
- The Way Forward:
- Final Thoughts:
- FAQ
Fundamental Rights are basic human freedoms guaranteed by the Constitution to protect citizens from arbitrary actions of the State. They create a balance between individual liberty and governmental power. In a diverse country like India, where differences in religion, caste, language, culture, and region exist, these rights act as a unifying force. They ensure that every citizen, regardless of background, is treated with fairness and respect.
Historical Evolution of Fundamental Rights:
The concept of Fundamental Rights has evolved through centuries of political and social struggles. Early constitutional documents such as the Magna Carta in England laid the groundwork for limiting the power of rulers. Later, the American Bill of Rights and the French Declaration of the Rights of Man emphasized liberty, equality, and fraternity. These ideas influenced modern constitutional democracies across the world.
In India, the demand for guaranteed rights gained momentum during the freedom struggle. Leaders recognized that independence from colonial rule would be incomplete without safeguarding civil liberties. Various committees and constitutional proposals stressed the need for enforceable rights to protect citizens from injustice. When the Constitution was adopted in 1950, Fundamental Rights were included as enforceable provisions under Part III, reflecting the vision of a just and democratic society.
The framers of the Constitution believed that democracy must provide not only political rights but also protection against discrimination and exploitation. They carefully designed these rights to address India’s social realities while ensuring harmony and progress.
Nature and Features of Fundamental Rights:
Fundamental Rights possess certain unique characteristics. First, they are justiciable, meaning citizens can approach courts if these rights are violated. Second, they are binding on the State, preventing misuse of authority. Third, they are not absolute and can be reasonably restricted to maintain public order, morality, and national security.
These features ensure that rights are both protected and balanced. Absolute freedom without restrictions could lead to chaos, while excessive restrictions could suppress liberty. Therefore, the Constitution carefully maintains equilibrium between freedom and responsibility.
Right to Equality: Cornerstone of Justice
The Right to Equality guarantees equality before the law and equal protection of laws. It prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth. In a society historically affected by social hierarchies, this right plays a transformative role.
Equality before the law ensures that no person is above legal accountability. Public officials, political leaders, and ordinary citizens are subject to the same legal standards. This principle strengthens trust in the judicial system.
The Constitution also allows special provisions for socially and educationally backward classes to promote equal opportunities. Such measures aim to reduce historical disadvantages and create a more inclusive society. Thus, equality is not merely theoretical but aims at practical justice.
Right to Freedom:
Expression of Democratic Spirit
Freedom is central to democratic life. The Right to Freedom includes freedoms of speech and expression, peaceful assembly, association, movement, residence, and profession. These freedoms allow individuals to develop their personality and contribute to national progress.
Freedom of speech enables citizens to express opinions, criticize government actions, and participate in public debates. A vibrant democracy depends on open discussions and diverse viewpoints. Media freedom, academic research, and public activism flourish under this right.
Freedom of movement and residence fosters national integration by allowing citizens to live and work anywhere in the country. Freedom of profession encourages economic growth and innovation, enabling individuals to pursue careers according to their interests and skills.
However, these freedoms are subject to reasonable restrictions to ensure that they do not threaten public order or security. The balance between liberty and discipline is essential for social harmony.
Right against Exploitation:
Protection of the Vulnerable
The Right against Exploitation prohibits human trafficking, forced labor, and child labor in hazardous occupations. It recognizes the inherent dignity of every human being.
Forced labor and trafficking violate basic human rights. By making such practices unconstitutional, the State affirms its commitment to justice and humanity. Prohibition of child labor in dangerous industries ensures that children receive education and protection.
This right highlights that economic development must not come at the cost of human suffering. It strengthens the moral foundation of democracy by safeguarding the weak and marginalized.
Right to Freedom of Religion:
Upholding Secular Values
India’s diversity includes numerous religions and faith traditions. The Right to Freedom of Religion guarantees individuals the freedom to profess, practice, and propagate religion.
The principle of secularism ensures equal respect for all religions. The State does not favor any particular faith. This fosters peaceful coexistence and unity.
Religious freedom, however, is subject to public order, morality, and health. Practices that harm social harmony can be regulated. This ensures that one’s freedom does not infringe upon the rights of others.
Cultural and Educational Rights:
Preserving Identity
Cultural and Educational Rights protect the interests of minorities by allowing them to preserve their language, script, and culture. Minority communities can establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
These rights promote inclusiveness and reassure communities that their heritage will be respected. Cultural diversity enriches national identity and strengthens unity.
Right to Constitutional Remedies: Enforcement Mechanism
The Right to Constitutional Remedies empowers citizens to approach higher courts for enforcement of their rights. Courts can issue writs to prevent injustice and misuse of authority.
This right ensures that Fundamental Rights are practical and enforceable. Judicial review acts as a safeguard against arbitrary actions. It strengthens the rule of law and accountability.
Without remedies, rights would remain symbolic. Therefore, this provision is essential for effective democracy.
Judicial Interpretation and Expansion:
Over time, courts have expanded the scope of Fundamental Rights. The Right to Life has been interpreted to include dignity, privacy, clean environment, and legal aid.
Judicial activism has played a significant role in protecting civil liberties. Public Interest Litigations have allowed citizens to seek justice for broader social causes.
This evolving interpretation ensures that rights remain relevant in changing times.
Role in Social Transformation:
Fundamental Rights have supported social reforms such as abolition of untouchability, gender equality, and protection of marginalized communities.
Legal recognition of equality has empowered women and disadvantaged groups. Environmental protection has been strengthened under the right to life.
Thus, Fundamental Rights function as instruments of progressive change.
Contemporary Relevance in the Digital Era:
Technological advancements have created new challenges. Issues like data privacy, cyber security, and online speech require reinterpretation of rights.
Recognition of privacy as a fundamental right reflects adaptation to modern realities. Digital platforms have expanded freedom of expression but also raised concerns about misinformation.
Balancing digital liberty with accountability is essential for democratic stability.
Challenges in Realization:
Despite constitutional guarantees, challenges persist. Lack of awareness prevents many citizens from exercising their rights effectively. Poverty and inequality limit access to justice.
Judicial delays and administrative inefficiencies weaken enforcement. Balancing national security with civil liberties remains complex.
Addressing these issues requires institutional reforms and civic education.
Fundamental Rights and Democratic Culture:
Democracy is not limited to elections. It requires respect for dissent, tolerance of diverse opinions, and active citizen participation.
Fundamental Rights nurture democratic culture by encouraging dialogue and accountability. They ensure that government remains answerable to the people.
An informed and vigilant citizenry is essential for sustaining these freedoms.
Global Context:
International human rights frameworks reflect similar principles of liberty and equality. Democratic nations worldwide recognize the necessity of protecting civil liberties.
India’s constitutional framework stands as a comprehensive model of rights protection, combining flexibility with stability.
The Way Forward:
To strengthen Fundamental Rights, legal awareness must be promoted. Educational institutions should emphasize constitutional values. Judicial reforms can improve access to justice.
Citizens must exercise rights responsibly and fulfill their duties. Cooperation between government, judiciary, and civil society is essential.
Final Thoughts:
Fundamental Rights are the pillars of democracy. They protect liberty, ensure equality, uphold dignity, and promote justice. They limit State power while empowering citizens.
In a diverse nation, these rights create unity while respecting differences. They adapt to changing circumstances and continue to guide democratic governance.
The true strength of a democracy lies in its commitment to protecting individual freedoms. By safeguarding Fundamental Rights, a nation secures justice, harmony, and progress for present and future generations.
FAQ
1. What are Fundamental Rights?
Fundamental Rights are basic human freedoms guaranteed by the Constitution to protect citizens from arbitrary actions of the State.
2. Why are Fundamental Rights important in a democracy?
They ensure equality, liberty, justice, and dignity, which are essential for democratic governance.
3. Can Fundamental Rights be restricted?
Yes, they can be reasonably restricted in the interest of public order, morality, security, and national integrity.
4. What is the Right to Constitutional Remedies?
It allows citizens to approach higher courts if their Fundamental Rights are violated.
5. How have courts expanded Fundamental Rights?
Courts have interpreted rights broadly to include privacy, clean environment, legal aid, and the right to live with dignity.